Contrary to popular belief, ancient India was vastly progressive in their ways. Unashamed of sexuality and quite open to the ideas of science, it’s amazing how ahead of the country’s history was when it came to understanding the ambiguous nature of morality. Which throws into light something very offensive about the moral policing that is rampant in our society today.
Because we realize that not only are these acts entrenching on our personal freedoms but also that those who commit them are completely ignorant of our ancient culture. The truth is the new age prudishness of India is actually something we’ve inherited from the British and less from our nation’s rich and diverse cultures! Here are a few reasons why we believe we had the moral high ground then and not now.
1. Marijuana
Not only was ancient India fine with the getting high on some sweet weed, we celebrated the plants very existence. The Vedas call cannabis a source of happiness, joy-giver, liberator that was compassionately given to humans to help us attain delight and lose fear. In fact, the plants main endorser is Lord Shiva himself. Which is probably why even now the Kumbh Mela is filled with sadhus getting high on the good green!
2. Divorce
While many are led to believe that divorce is an unheard of thing in Indian culture, the Arthashastra contains ‘rules for divorce’ which shows that divorce was indeed a part of daily life in ancient India. So yeah, divorce was acceptable for normal people then and not just Bollywood celebrities like it is now!
3. Atheism
The Cārvāka‘s were an ancient Hindu sect that actually followed the principles of Atheism. Bhattacharya posits that Cārvāka may have been one of several atheistic, materialist schools that existed in ancient India. Unlike now where atheists are looked upon as godless rebels, ancient India embraced even the view point of the unbelievers.
4. Transgenders
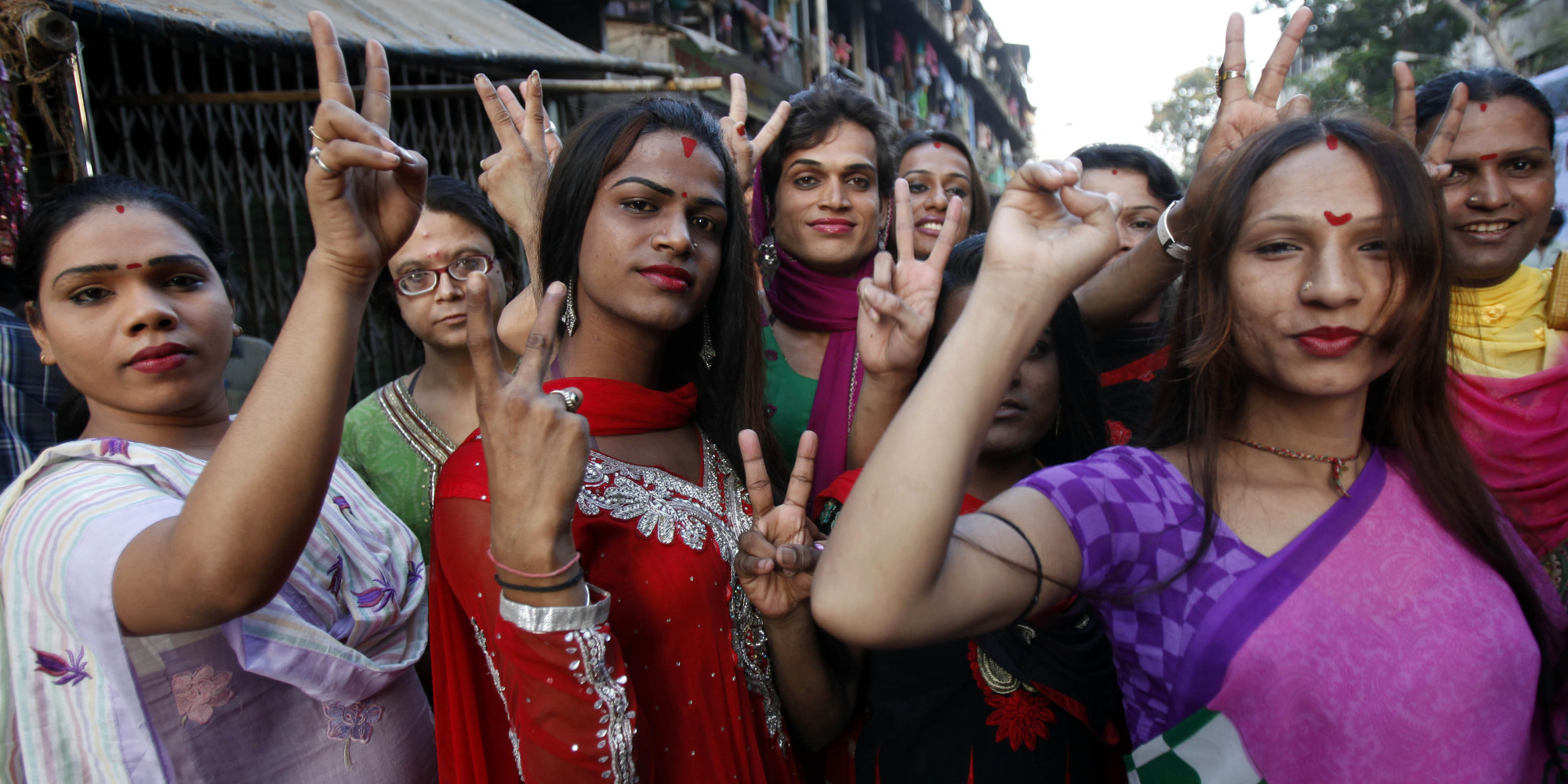

Ancient India was completely fine with the idea of transgenders. There are even gods solely dedicated for them. Arjuna himself was in drag for the whole time the Pandavas were in hiding!
5. Sex
Ancient India was extremely liberated sexually. From works of art like the Kamasutra, which is a detailed look at the act of copulation to a game named ‘Ghatkancuki’ where some chosen elite men and women were made to indulge in sexual acts for the entertainment of the audience, we were a pretty wild bunch. And to think we frown down on premarital sex now in India because it’s against our culture.
6. Gambling
Gambling has been a part of India since way back. Kings and ministers who regularly gambled are strewn across the pages of ancient Indian literature. In the 15th-century betting, houses were made legal and a share of the profits was given to the king!
ALSO READ : 10 Reasons You Should Participate In No-Shave November – Women Too!
7. Psychedelics
Soma, a concoction with psychedelic properties was a major part of Vedic rituals. It is described as being prepared by extracting juice from the stalks of a certain plant. In his book Food of the Gods Terrance Mckenna speculates that Soma could’ve been psychedelic mushrooms.
8. Brothels
Prostitution was extremely prevalent in ancient India and was actually legal. In the Arthashastra providing sexual entertainment to the public using prostitutes (ganika) was an activity not only strictly controlled by the State but also one which was, for the most part, carried on in state-owned establishments. Geez, talk about a liberal viewpoint on a relevant social issue!
9. Science
Unlike our Western counterparts, in ancient India, religion never stood in the way of scientific thinking. Math and physics were an integral part of ancient India. Unlike the rudimentary and temporary infrastructure of today, ancient India put a lot of thought and math into architecture and water storage. Ayurveda was an intense study of the human body and natural medicines that could cure ailments. So it’s safe to say we were a scientifically curious culture.
10. Polyamorous / Polygamous Relationships
Although not popular, polygamy was prevalent in ancient India among the warrior castes. Pandu, the father of the Pandavas in Mahabharata had two wives Kunti and Madri. Krishna, considered one of the incarnations of Vishnu, had eight chief wives and Draupadi was married to all five of the Pandavas.
11. Art
Freedom of expression was rarely censored in ancient India. With sculptors and paintings of rampant nudity adorning the walls of temples in Khajuraho and many other places, we literally celebrated our lack of censorship. Music and dance was also religiously practiced all over the country. And to think religious fanatics don’t allow paintings of Gods in the name of culture in present India!
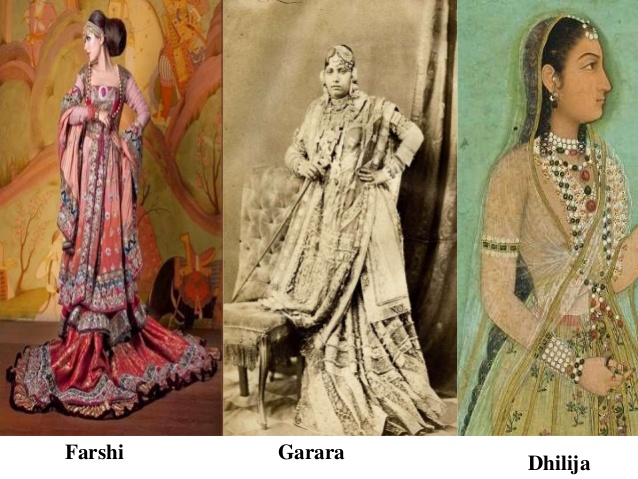
12. Fashion
With a variety of fabrics and a liberal viewpoint, ancient India was quite ahead with its fashion statement. Scantily clad women and bejeweled men never attracted any moral policing in those days as they do now in the name of culture.
Tell us what you think in the comments below.